-
The Cablevision nDVR Decision: Winners, Losers and How it Relates to Broadband
Last Monday's decision by the Second Circuit Court of Appeals, reversing a lower court's March 2007 ruling that Cablevision's plan to deploy a Network Digital Video Recorder (nDVR) violated copyright law has huge potential implications across the video landscape. DVR, Video on Demand and broadband video are all close cousins jockeying for position in the race to provide on-demand choice to consumers. So for those interested in broadband's deployment, it's important to understand ongoing developments in DVR and VOD as well.
Today, I'm pleased to have Mugs Buckley and Colin Dixon, analysts at The Diffusion Group weigh in with their thoughts on last week's ruling.
The Cablevision nDVR Decision: Winners, Losers and How it Relates to Broadband
by Mugs Buckley and Colin Dixon, The Diffusion Group
The August 4th Cablevision nDVR decision by the Second Circuit Court of Appeals opens up the
 possibility that the company will be able to move ahead with its original nDVR plan, much to the dismay of the plaintiffs, a group of major studios and TV broadcasters. For a primer on the significance of the decision, we offer the following thoughts:
possibility that the company will be able to move ahead with its original nDVR plan, much to the dismay of the plaintiffs, a group of major studios and TV broadcasters. For a primer on the significance of the decision, we offer the following thoughts:WHAT'S AN nDVR vs. a DVR?
The root of the nDVR case is where a TV viewer's recorded show gets stored: on a hard drive in a DVR located in the home (as is the current model) or on a hard drive in a cable operator's network (as Cablevision and other network operators prefer).
WHY DOES IT MATTER?
To the viewer, it doesn't; since using either approach allows recording and playback of programs.
But since the correlation between digital recording and ad-skipping is well-documented, the studios' and networks' key concern is that nDVR could dramatically accelerate recording usage, thereby accelerating the ad-skipping trend. That would be a big blow to their economic model. For Cablevision and other operators, it's all about cost. Storage in the network is much cheaper than a truck roll to a customer's home and individual DVR box deployments. nDVR also allows the operator to leverage their huge investment in VOD systems.
WHERE DO THINGS GO FROM HERE?
While Cablevision won its appeal, the ruling is far from conclusive. The next step is for the lower court to revisit this ruling, so when Cablevision will actually be able to roll out the nDVR service is totally unknown. They must wait for the lower court to decide if they agree with the upper court's decision, which is not expected before the end of 2008. And of course we expect the studios and content providers to file subsequent appeals.
WHERE DO OTHER OPERATORS STAND?
If Cablevision wins, other cable and telco network operators will implement nDVR too. For example, Time Warner Cable's CEO Glenn Britt told Multichannel News on August 6th, "We've said for a long time that a centralized network DVR is a better engineering solution than having hard drives all over everybody's home. If this particular court case is upheld, we will deploy that."
AND THE BROADBAND IMPLICATIONS?
Should the ruling stand, a company like TiVo could possibly be able to capitalize on it by delivering the nDVR experience over broadband. Of course, TiVo's been shifting its model to work with service providers anyway, so this may not be a strategy it would pursue.
As for other broadband implications, this is where the interplay between nDVR, VOD and broadband video can get murky. For instance, sites like Hulu and ABC.com are already storing programs in the network (albeit in a way that they control) for on-demand consumption. This obviates the requirement that the consumer take the action to record say the latest episode of "The Office" in a DVR or nDVR environment.
And of course, the content providers control the ad insertion (although presumably they could do that for nDVR as well). Other than making ALL TV programs available vs. just the subset currently available for broadband delivery (and VOD) and the fact that nDVR can be viewed easily on TVs, which is not currently the case for broadband, the differences between nDVR and broadband start to feel quite blurry.
As you can see, nDVR has lots of implications for everyone in the video value chain.
Bottom line: Much more to come. Stay tuned.
Categories: Broadcasters, Cable TV Operators, Studios
Topics: Cablevision, Network DVR
-
Get Ready for the "Broadband Olympics"
At last, the 2008 Beijing Summer Olympics are upon us. In addition to the many extraordinary athletic performances we can expect, I believe this year's Games will be considered the first "Broadband Olympics." This potentially seminal event for the broadband medium was on my list of "6 Broadband Predictions for 2008."
Through NBC's massive investment in broadband coverage, consumers are going to enjoy a completely
 different Olympic experience, obsoleting many of our traditional responses around missing key Olympic moments: "I just couldn't stay up so late to see that one" or "Hopefully they'll replay that one, I'd really like to see it, or "My kids wanted to see that one but it was during school."
different Olympic experience, obsoleting many of our traditional responses around missing key Olympic moments: "I just couldn't stay up so late to see that one" or "Hopefully they'll replay that one, I'd really like to see it, or "My kids wanted to see that one but it was during school." It's hard to imagine a sporting event, or any other event for that matter, better suited to broadband coverage. The two key challenges of Olympic broadcast coverage have always been the limited shelf space that just one broadcast channel provides (leading to coverage of only the most popular sports, and even then mainly the final rounds) and the time zone differences, which have created an awkward scheduling mix for U.S. prime-time.
NBC, which has been touting its broadband Olympics coverage for months, has addressed these by offering a package of 2,200 hours of live streaming and 3,000 hours of on-demand highlights. The scale of NBC's broadband undertaking is unprecedented, and will easily create a new case study for future broadband event producers.
To get a little glimpse of how just the on-demand portion of coverage will work, yesterday I spoke with Anystream's CEO Fred Singer and COO Bill Holding. Anystream is a key media production and publishing partner of NBC's, essentially handling all of the work flows for the 10,000 video assets that will be available on-demand.
Fred and Bill gave me a sense of the massive complexity involved in ingesting video from the other side of the planet, processing it in a fraction of the customary time allowed, and then distributing it within minutes - according to an elaborate set of rights and business rules - to 16 partners in multiple formats. Often I speak of the complexity involved in the Syndicated Video Economy; there is no better example than the distribution of Olympics' video.
 Meanwhile, the broadband Olympics will be a coming out party of sorts for Microsoft's Silverlight, the company's Flash-killer. Tens of millions of new downloads will be driven by the Olympics, and Silverlight's picture-in-picture, rewind and HD features will receive their initial real-world stress test.
Meanwhile, the broadband Olympics will be a coming out party of sorts for Microsoft's Silverlight, the company's Flash-killer. Tens of millions of new downloads will be driven by the Olympics, and Silverlight's picture-in-picture, rewind and HD features will receive their initial real-world stress test.Lastly of course, there are all of us consumers. While unprecedented coverage is available at NBCOlympics.com and elsewhere, to actually enjoy it entails getting down the learning curve of what, where, when and how individual sports will be offered. In short, massive choice requires consumer involvement. Nevertheless, I expect we'll be hearing about some very impressive broadband stats from NBC over the next two weeks and thereafter.
Let the Games begin!
Categories: Broadcasters, Sports
Topics: Anystream, NBC, Olympics
-
Non-Linear Presentation + Long-form Premium Video = Big Opportunity
I continue to be surprised that more long-form premium content providers have not pursued initiatives to slice and dice their programs into a non-linear user presentation. This is what "The Daily Show" has done at its site, deconstructing every episode into searchable clips. I think it's a big opportunity to drive more fan engagement, new ad inventory and provide insight about new programming ideas.
While this idea is a natural for archived sports and news programming, I think the model applies to scripted programs as well. Here's an example:
As I've written before, my wife and I were huge fans of "The West Wing" during its seven-year run on NBC.
 While we now own the full DVD collection, periodically I'll talk to someone about the show and reminisce about a specific moment from years back. (In fact, TWW seems cosmically related to the current election cycle, given the show's last narrative around 2 candidates - one younger and one older - battling to succeed Bartlet.) This spurs many of those, "boy, I'd love to see that scene right now!" moments.
While we now own the full DVD collection, periodically I'll talk to someone about the show and reminisce about a specific moment from years back. (In fact, TWW seems cosmically related to the current election cycle, given the show's last narrative around 2 candidates - one younger and one older - battling to succeed Bartlet.) This spurs many of those, "boy, I'd love to see that scene right now!" moments.So wouldn't it be awesome if NBC or Warner Bros. (its producer), or whoever has the rights, were to create a site where all the episodes were archived and fully indexed for searching? This would go far beyond the show's current lame-o web site. I could type in "Bartlet speeches," "Josh meltdowns" or even "C.J.-Danny fights" and instantly see collections of relevant clips.
Before you accuse me of being geeky, stop and consider that we all have our favorite programs and love to relive memorable lines and moments. I'd argue that a really vibrant community could be built at these sites, attracting traditional advertisers eager to continue their audience relationships. Then of course there's the opportunity to embed clips into Facebook and MySpace pages, extending the community further. And think about what this ongoing loyalty would do to drive up the value of broadcast syndication rights.
The big challenge here is indexing the archive. The process must rely heavily on accurate metadata generation, but in a highly scalable, cost-effective manner. That's a mouthful of requirements, so clearly this isn't easy stuff. Various players are trying to crack this nut; two which I've previously written about are Gotuit (which is announcing a partnership with Move Networks today) and EveryZing, but there are others too. Recently I've had briefings with 2 companies that are investing in this area and will have news in the coming months.
Long-from premium providers are facing an onslaught of competition from short-form alternatives while also commonly experiencing a shortage of available inventory. Non-linear presentations of their content addresses both these issues, while delighting loyal fans. I see this as an emerging and sizable opportunity.
Am I missing something here? Post a comment now!
Categories: Advertising, Broadcasters, Technology
Topics: Daily Show, EveryZing, Gotuit, Move Networks, NBC, Warner Bros., West Wing
-
Great Webinar on Syndicated Video Yesterday
I participated in a great webinar on the syndicated video economy yesterday, along with Greg Clayman, EVP Digital Distribution and Biz Dev at MTV Networks and Suzanne Johnson, Senior Industry Marketing Manager at Akamai Technologies.
The three presentations were very complimentary: I laid out the framework of the syndicated video economy, Greg provided tangible examples of how MTV's capitalizing on it, and Suzanne addressed how Akamai is helping enable it. We had a huge audience and lots of great follow-up questions. If you're interested in content syndication, I highly recommend listening in.
The webinar is available for replay by clicking here
(Note if you previously registered, you should have an email from "Digitally Speaking" which gives you details of how to access the webinar, so you don't have to re-register)
Categories: Events, Syndicated Video Economy
-
Citysearch Offering Local Merchants Video Enhancement
Citysearch, the big online local information company, is making an aggressive push into video. The company is currently running a new promotion which allows its merchants to have a complimentary video made for them, which enhances their Citysearch listing, and can also be used on their own web site and on YouTube.
I'm always on the lookout for ways video can drive more revenue, and Citysearch's effort (originally begun in early '07) qualifies on at least two levels. First, it's a valuable enhancement to Citysearch's pay-for-performance ad model, increasing the ARPU the company derives from its merchants. Second, it appears to be a bona fide differentiator for merchants in helping them attract new business. And of course it helps deliver on users' growing expectations for video experiences.
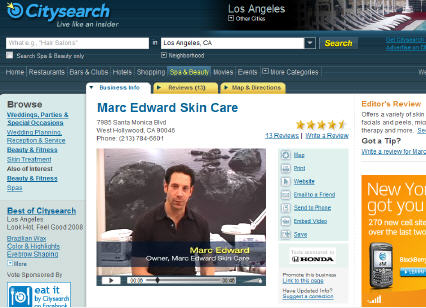
Last week I spoke with Brian McCarthy, Citysearch's VP of Merchant Product to learn more about how the program works. I also spoke to Marc Edward, who runs Marc Edward Skincare in West Hollywood, CA, which is a merchant that's been offering video in its Citysearch listing for over a year.
Under the current promotion, Citysearch will make a 60-90 second video for its merchants for no cost to them. Citysearch has partnered with 3 production firms, TurnHere, StudioNow and GeoBeats to produce the video, which Brian said cost under $1,000 apiece. The merchant is involved in the editing process and then the video is added to the merchant's listing. When a user watches the video for at least 10 seconds, the merchant is charged a fee ranging from $.40 to $2.00, as part of Citysearch's "multimedia package."
Marc was one of the early users of Citysearch video and is quite enthusiastic about the results. He feels that nothing can convey what his business is about better than prospects actually seeing him talk about it, and explaining what they can expect. While he hasn't tracked new business directly to the video he offers, anecdotally he said new clients mention and cite the video as a major reason why they chose his shop over others.
While it's still early days for video enhancements in local listings/search results, it seems like a natural way to extend the model. Other local players like WorldNow, CBS and other broadcasters are on to this as well. The key is getting the financial model right for all parties: who pays to get the video made and how it generates a return over time. Citysearch seems to be making progress proving how the model can work.
What do you think? Post a comment now.
Categories: Advertising
Topics: CBS, CitySearch, GeoBeats, StudioNow, TurnHere, WorldNow
-
comScore Revises YuMe Traffic Down
Back on July 22nd I passed on news from comScore that YuMe had broken into the top 10 ad networks, reaching almost 135 million unique visitors in June. Not so fast it turns out. As reported well by both
 NewTeeVee and Online Media Daily over the few days, comScore has quietly revised YuMe's reach down to 59.2 million uniques, which would actually land it at number 32 on comScore's June Ad Focus report.
NewTeeVee and Online Media Daily over the few days, comScore has quietly revised YuMe's reach down to 59.2 million uniques, which would actually land it at number 32 on comScore's June Ad Focus report. The change results from re-assigning some traffic from major YuMe client MSN. comScore had given YuMe credit for all of MSN's page views, when in fact YuMe was only serving ads on certain sections of the portal. So comScore has decided it's more accurate to give YuMe credit solely for those pages.
Needless to say, YuMe is not happy about the change and is protesting the new numbers. Its argument is
 that with comScore's revised approach, YuMe traffic is being counted differently than all other ad networks. For now it continues to prominently showcase the original comScore numbers on its home page. YuMe seems determined to see a revision to the revision, so we'll all have to see what comScore does next.
that with comScore's revised approach, YuMe traffic is being counted differently than all other ad networks. For now it continues to prominently showcase the original comScore numbers on its home page. YuMe seems determined to see a revision to the revision, so we'll all have to see what comScore does next. There are many posts on VideoNuze about the various ad networks and how they seek to differentiate from each other. Traffic is certainly one of the key battlegrounds, so it's no surprise this skirmish has broken out over the comScore numbers. One is tempted to feel some sympathy for media buyers...if the measurement firms haven't yet figured out how to accurately count the networks' relevant traffic, how are the agencies expected to buy on behalf of their clients?
Categories: Advertising
-
Join Me at VideoSchmooze in Boston on Tuesday, Sept. 9th
I'm very pleased to announce VideoNuze's first VideoSchmooze networking event, to be held in Boston on
 Tuesday, Sept. 9th. The event is complimentary and will be at Vinalia from 6-9pm. Early registrants will receive a drink ticket (cash bar to follow) and there will be plenty of hors d'oeuvres for everyone.
Tuesday, Sept. 9th. The event is complimentary and will be at Vinalia from 6-9pm. Early registrants will receive a drink ticket (cash bar to follow) and there will be plenty of hors d'oeuvres for everyone.As many of you know, there are countless early stage and established broadband video-related companies in the Boston area. For a while I've been eager to get this community together to mix it up. VideoSchmooze will be a premier opportunity for executives, entrepreneurs, investors and other decision-makers to meet up and swap ideas. And yes - out-of-towners are welcome!
VideoSchmooze is generously underwritten by Flybridge Capital Partners, Atlas Venture, Goodwin Procter and Silicon Valley Bank.
Categories: Events
Topics: VideoSchmooze
-
The FCC's Comcast Sanction: More Problems, Fewer Solutions Ahead
In case you missed it, last Friday the FCC took the unprecedented step of sanctioning Comcast for what it considered unreasonable network management policies. Before you deem this "inside-the-beltway" bureaucratic wrangling and click away to your next piece of business, I suggest you take a moment to consider the broad-reaching implications of the FCC's action, and how they will undoubtedly affect you and your video business long-term.
(If you'd really like to dig in, the FCC commissioners' opinions are here)
There has been a lot written about what precipitated the FCC's action, so I won't restate all the gory details here. Very briefly, last Fall formal complaints were filed with the FCC alleging that Comcast treated certain of its broadband subscribers' use of BitTorrent, a peer-to-peer (P2P) application, in a discriminatory manner vis-a-vis other network traffic.
After collecting comments and taking testimony from experts, the FCC concluded (with its Republican
 chairman leading the charge) to sanction, but not fine, Comcast for its actions. Importantly, it also stipulated that Comcast has to submit its network management plans to the FCC going forward, effectively anointing the FCC as the nation's new broadband network management czar.
chairman leading the charge) to sanction, but not fine, Comcast for its actions. Importantly, it also stipulated that Comcast has to submit its network management plans to the FCC going forward, effectively anointing the FCC as the nation's new broadband network management czar. I submit that for those in the broadband video industry, nothing good will come from the FCC's action. The FCC and other governmental bodies are understaffed and ill-equipped to be making highly technical network management decisions. The FCC's decree may well usher in an era of confusion and sclerotic decision-making, forcing broadband ISPs to curtail network investments at exactly the time when they need to be increasing their spending to enable more video traffic to flow.
It is worth noting that the Internet's periodic growing pains have been overcome not by the government stepping in, but by the government stepping away. This surely seems counter-intuitive to regulatory traditionalists. But it works because the ethos of the Internet's technical community is by and large collaborative and forward-looking. Supplanting that spirit with litigious, bureaucratic sprawl benefits nobody. In saying all this, I'm guided by pragmatism, not political bias.
Though we all want to be able to use the Internet free from any interference, the problem is that the Internet is still a wild west of sorts, where lawless and lawful behavior can be heavily intertwined. P2P is a perfect example. While legal (when used appropriately), its use can wreak havoc for other users and for network operators. Previously, there were no clear rules about how operators should respond when a handful of P2P users swamp the network. The Comcast sanction doesn't change that, it just puts the FCC in the position of judging, case-by-case the reasonableness of the network operator's containment actions.
So here we are. An odd stew including a militantly anti-cable FCC chairman, two flag-draped Democratic cohorts, a clutch of freedom of speech instigators and a large ISP (Comcast) which flunked PR 101 in how it implemented and communicated its network management practices, has opened up a new era in broadband regulatory policy. Ugh.
What do you think? Post a comment now!
Categories: Broadband ISPs, Regulation
Topics: BitTorrent, Comcast, FCC